INTRODUCTION
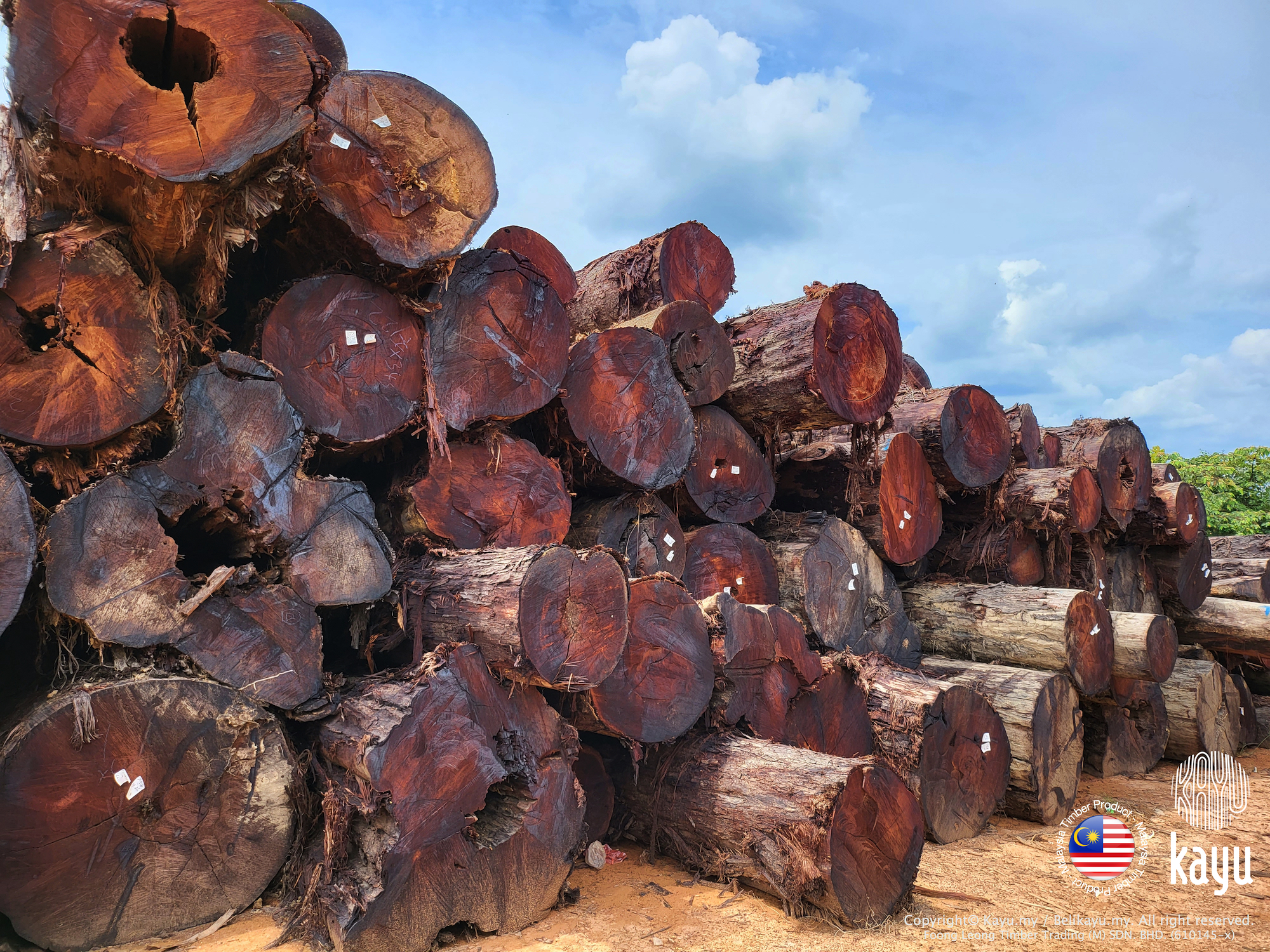
The Standard Malaysian Name for the heavy timbers of Hopea spp. (Dipterocarpaceae). Vernacular names applied include giam (Peninsular Malaysia) with various epithets, selangan (Sabah and Sarawak) with various epithets and other localised names too numerous to list here. Major species include H. ferrea, H. helferi, H. nutans, H. pentanervia and H. semicuneata. The sapwood is yellow and is poorly defined from the heartwood, which is yellow with a greenish tinge when fresh and turns deep red-brown on exposure.
Also known as Koki:r (Cambodia); Balau (Indonesia); Hin, Mai khaen fay and Mai la en (Laos); Thingyan (Myanmar); Heavy hopea (Papua New Guinea); Saplungan and Yakal (Philippines); Krabok-krang, Lao Tao, Takian Hin, Takian-Nu and Takian-rak (Thailand); and Sao xanh (Vietnam).
DENSITY
The timber is a Heavy Hardwood with a density of 865-1,220 kg/m3 air dry.
NATURAL DURABILITY
Only one species of giam (H. nutans) has been subjected to the graveyard test to determine its natural durability under exposed conditions. Of the 59 samples tested (dimension 50 mm x 50 mm x 600 mm), all were still serviceable after two years; only 5 per cent of the test sticks were destroyed in the eighth year and 80 per cent of the test sticks were found to be still serviceable after the fourteenth year. Compared to other Heavy Malaysian Hardwoods tested under the same conditions e.g. chengal, balau and merbau, this particular species of giam seems to be more durable. The timber has therefore, been classified as very durable under Malaysian conditions (Jackson, 1960).
PRESERVATIVE TREATMENT
Desch (1957) recorded that the timber, particularly the heartwood region, is exceptionally difficult to treat with preservatives. But for a timber which is naturally durable, preservative treatment is normally unnecessary.
TEXTURE
Texture is very fine to moderately fine and even, with deeply interlocked grain.
STRENGTH PROPERTIES
The timber falls into Strength Group A (Engku, 1988).
Strength Properties of Giam
Species | Test Condition | Modulus of Elasticity(MPa) | Modulus of Rupture(MPa) | Compression parallel to grain (MPa) | Compression perpendicular to grain (MPa) | Shear strength(MPa) |
H. nutans | Green | 17,900 | 109 | 67 | 13 | 13 |
H. helferi | Green | 14,600 | 103 | 54 | 10 | 14 |
Air dry | 16,500 | 122 | 59 | 11 | 16 |
MACHINING PROPERTIES
It is easy to difficult to resaw and cross-cut. Planing is, however, easy and the planed surface is smooth.
Machining Properties of Giam
Species | Test Condition | Sawing | Planing | Boring | Turning | ||||
Re-sawing | Cross Cutting | Ease of planing | Quality of finish | Ease of boring | Quality of finish | Ease of turning | Quality of finish | ||
H. helferi | Green | easy | easy | easy | smooth | easy | smooth | - | - |
Air dry | easy | easy | easy | smooth | easy | smooth | - | - | |
H. nutans | Green | slightly difficult | difficult | easy | smooth | slightly difficult | smooth | - | - |
Air dry | difficult | difficult | easy | smooth | slightly difficult | smooth | difficult | smooth to rough | |
NAILING PROPERTY
Nailing property is rated as very poor.
AIR DRYING
The timber seasons very slowly, with only slight end-checking, splitting and surface-checking as the main sources of degrade. 13 mm thick boards take approximately 6 months to air dry, while 38 mm thick boards take 8 months.
KILN DRYING
Kiln Schedule B is recommended.
Kiln Schedule B
Moisture Content (%) | Temperature (Dry Bulb) | Temperature (Wet Bulb) | Relative Humidity (%) (approx.) | ||
'F | 'C | 'F | 'C | ||
Green | 105 | 40.5 | 101 | 38.0 | 85 |
40 | 105 | 40.5 | 99 | 37.0 | 80 |
30 | 110 | 43.5 | 102 | 39.0 | 75 |
25 | 115 | 46.0 | 105 | 40.5 | 70 |
20 | 130 | 54.5 | 115 | 46.0 | 60 |
15 | 140 | 60.0 | 118 | 47.5 | 50 |
SHRINKAGE
Shrinkage is average to high, with radial shrinkage ranging 1.4-2% and tangential shrinkage ranging 2.6-4.4%.
DEFECTS
Though the form of the trees is sometimes poor, giam timber is generally free from major defects. Minor defects of the timber include occasional attack by 'pin' hole, powder post and longicorn beetles. Resin and bark pockets may also be found in the timber. The sapwood, which is light in colour, is sometimes attacked by sap-stain fungi.
USES
The timber is suitable for all heavy construction, marine construction, ship and boat building (keels, keelsons and framework), posts, beams, joists, rafters, flooring (heavy traffic), decking, fender supports, mallets, vehicle bodies (framework and floor boards), heavy duty furniture, cooling tower (structural members), power-line poles, railway sleepers, columns (heavy duty), door and window frames and sills, tool handles (impact), telegraphic and power transmission posts and cross arms, container floor boards and heavy duty laboratory benches.
Information shared by "mtc.com.my".
Giam
Sorry, there is no product in this collection